Database views are virtual tables which are built up using a SELECT query. The query may contain one or more tables.
To help explain database views, here is a quick script created using SQL Server to create some tables and data. (If you want to create the tables using MySQL, then substitute the part “IDENTITY(1,1)” with “AUTO_INCREMENT”)
[sourcecode language=’sql’]CREATE TABLE Department
(
ID TINYINT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1,1),
Department VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL
)
GO
CREATE TABLE Staff
(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
FirstName VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
LastName VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
Salary INT NOT NULL,
DepartmentID TINYINT NOT NULL REFERENCES Department(ID)
)
GO
INSERT INTO Department(Department)
VALUES(‘Sales’),(‘Finance’),(‘Technology’);
INSERT INTO Staff(FirstName, LastName, Salary, DepartmentID)
VALUES
(‘John’,’Smith’,50000,1)
,(‘Raymond’,’Jones’,50000,2)
,(‘Tracey’,’Carter’,50000,3);[/sourcecode]
So lets create a view of the data joining the two tables together and presenting certain fields.
[sourcecode language=’sql’]CREATE VIEW vwStaff
AS
SELECT
S.ID AS StaffID
, S.FirstName
, S.LastName
, D.Department
FROM Staff S
JOIN Department D ON S.DepartmentID = D.ID
GO
GRANT SELECT ON vwStaff TO application_developer;[/sourcecode]
Instead of selecting from the tables, the application developer would select from the view “vwStaff” to retrieve the data they needed.
SELECT * FROM vwStaff StaffID FirstName LastName Department ----------- -------------------- -------------------- -------------------- 1 John Smith Sales 2 Raymond Jones Finance 3 Tracey Carter Technology (3 row(s) affected)
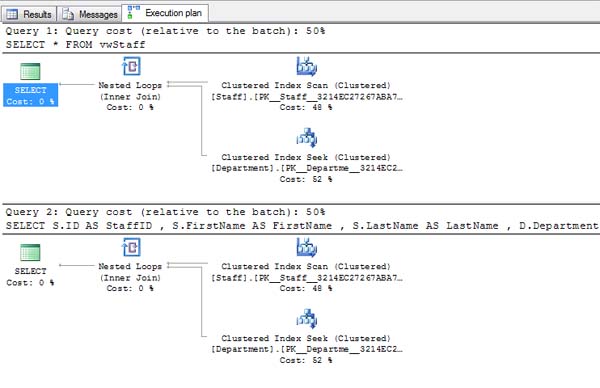
There is no performance difference between running the SQL or running database views. If you look at both SQL Server and MySQL, the execution plans are identical between the SQL and database views.
MySQL….
[sourcecode language=’sql’]mysql>
explain SELECT S.ID AS StaffID
, S.FirstName
, S.LastName
, D.Department
FROM Staff S
JOIN Department D ON S.DepartmentID = D.IDG;[/sourcecode]
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: S
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 3
Extra:
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: D
type: eq_ref
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 1
ref: dbadiaries.S.DepartmentID
rows: 1
Extra:
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
[sourcecode language=’sql’]mysql> explain SELECT * FROM vwStaffG;[/sourcecode]
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: S
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 3
Extra:
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: D
type: eq_ref
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 1
ref: dbadiaries.S.DepartmentID
rows: 1
Extra:
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
SQL Server….
Advantages of Database Views
- Data protection – create views to protect sensitive data. For example the salary column was hidden in my example above.
- Code re-use – simplifies application development. If some business logic changes for presenting data, change it once in the view and not many times in different places.
- Simplifies access to data for untrained users. Lets say you have a department of data analysts who are experts with Excel but can’t write SQL. Create them a view of the data and have them load that into Excel. They can’t write SQL but they can choose a view from a list of available datasets – everyone is happy.
- Performance – lets say your data analysts can write SQL but you don’t want them writing run-away queries which bring your database server down. Create them a view instead of allowing them direct access to the data.
- If you are using BCP to export data, you can format the data through views as BCP data formatting is rather limited.
- Working around non-deterministic function limitations.
Pitfalls of using Database Views
- Ease of use – you’re probably thinking, what’s he talking about? Well it is very easy to think “I’ll join to that view I created in the database to satisfy this new query I am writing”. You have to remember that database views are SELECT queries. Every time you run one or join to one, the query is run on the fly to produce the results of the view. As an author of a query and using the view above, if you only needed access to the data in the “Staff” table to form part of your query, why join to a view which pulls in data from the “Department” table? That is extra IO overhead which when dealing with large volumes of data or frequent batch requests can have negative performance implications. It is better to have access to either the table (if you are allowed to) or another view of the “Staff” table which allows you to view the fields which you require and use that.
- Nested database views – don’t create views based on other views as this has a negative performance impact. Better to create views from the base tables.

Good Article
Very great and clear article (talking as a views newbie)…